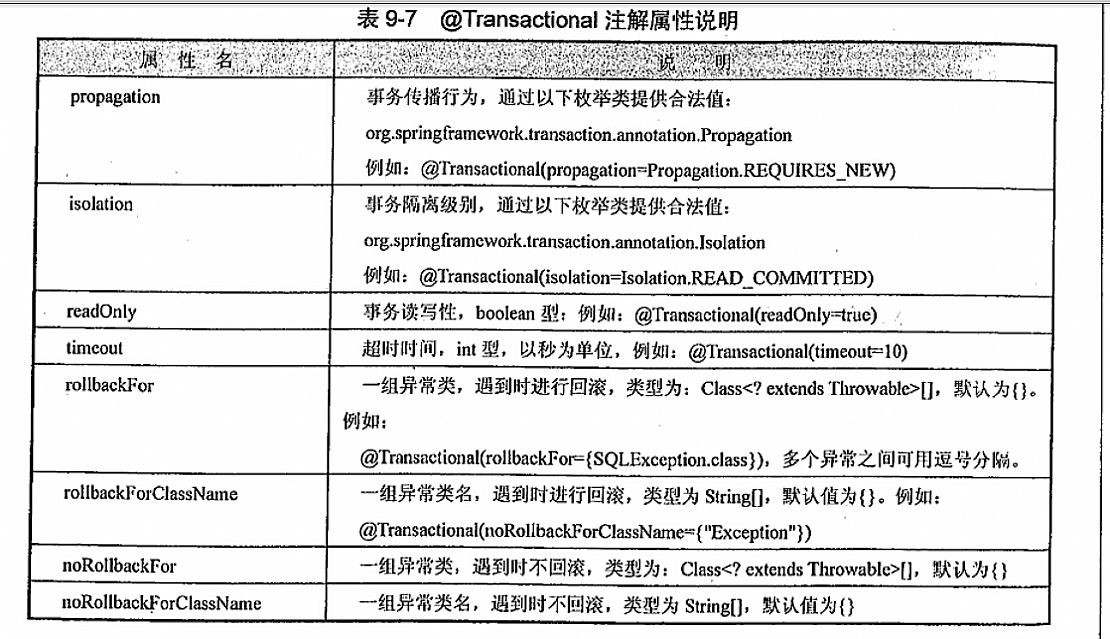
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Atomic(原子性) | 事务中包含的操作被看做一个逻辑单元,这个逻辑单元中的操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败。 |
| Consistency(一致性) | 只有合法的数据可以被写入数据库,否则事务应该将其回滚到最初状态。 |
| Isolation(隔离性) | 事务允许多个用户对同一个数据进行并发访问,而不破坏数据的正确性和完整性。 同时,并行事务的修改必须与其他并行事务的修改相互独立。 |
| Durability(持久性) | 事务结束后,事务处理的结果必须能够得到固化。数据库肯定是要被广大客户所共享访问的, 那么在数据库操作过程中很可能出现以下几种不确定情况。 |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| 读脏 | 一事务对数据进行了增删改,但未提交,有可能回滚, 另一事务却读取了未提交的数据,允许脏读取,但不允许更新丢失。 如果一个事务已经开始写数据,则另外一个事务则不允许同时进行写操作, 但允许其他事务读此行数据 |
| 不可重复读 | 一事务对数据进行了更新或删除操作,另一事务两次查询的数据不一致 |
| 幻读 | 一事务对数据进行了新增操作,另一事务两次查询的数据不一致 |
| 隔离级别 | 隔离级别的值 | 导致的问题 |
|---|---|---|
| Read-Uncommitted | 0 | 导致脏读 |
| Read-Committed | 1 | 避免脏读,允许不可重复读和幻读 |
| Repeatable-Read | 2 | 避免脏读,不可重复读,允许幻读 |
| Serializable | 3 | 串行化读,事务只能一个一个执行,避免了脏读、不可重复读、幻读。 执行效率慢(我遇到过一种情况,用时是隔离级别1的30倍),使用时慎重 |
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未提交读 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 已提交读 | 否 | 是 | 是 |
| 可重复读 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 可序列化 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
隔离级别越高,越能保证数据的完整性和一致性,但是对并发性能的影响也越大。
大多数的数据库默认隔离级别为 Read Commited,比如 SqlServer、Oracle
少数数据库默认隔离级别为:Repeatable Read 比如: MySQL InnoDB
参考文档:数据库事物隔离级别通俗理解
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| ISOLATION_DEFAULT | 这是一个 PlatfromTransactionManager 默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别。另外四个与 JDBC 的隔离级别相对应。 |
| ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED | 这是事务最低的隔离级别,它充许令外一个事务可以看到这个事务未提交的数据。这种隔离级别会产生脏读,不可重复读和幻像读。 |
| ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED | 保证一个事务修改的数据提交后才能被另外一个事务读取。另外一个事务不能读取该事务未提交的数据。 |
| ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ | 这种事务隔离级别可以防止脏读,不可重复读。但是可能出现幻像读。它除了保证一个事务不能读取另一个事务未提交的数据外,还保证了避免下面的情况产生(不可重复读)。 |
| ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE | 这是花费最高代价但是最可靠的事务隔离级别。事务被处理为顺序执行。 |
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择,也是 Spring 默认的事务的传播。 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
以下解释的场景都是基于 ServiceA.methodA() 里调用 ServiceB.methodB()
加入当前正要执行的事务不在另外一个事务里,那么就起一个新的事务。
比如说,ServiceB.methodB() 的事务级别定义为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。
执行 ServiceA.methodA() 是它已经起了事务,这时调用 ServiceB.methodB(),ServiceB.methodB() 看到自己已经运行在 ServiceA.methodA() 的事务内部,就不再起新的事务。
假如 ServiceB.methodB() 运行的时候发现自己没有在事务中,他就会为自己分配一个事务。
这样,在 ServiceA.methodA() 或者在 ServiceB.methodB() 内的任何地方出现异常,事务都会被回滚。
比如我们设计 ServiceA.methodA() 的事务级别为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ServiceB.methodB() 的事务级别为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW。
那么当执行到 ServiceB.methodB() 的时候,ServiceA.methodA() 所在的事务就会挂起,ServiceB.methodB() 会起一个新的事务,等待 ServiceB.methodB() 的事务完成以后,它才继续执行。
他与 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 的事务区别在于事务的回滚程度了。因为 ServiceB.methodB() 是新起一个事务,那么就是存在两个不同的事务。如果 ServiceB.methodB() 已经提交,那么 ServiceA.methodA() 失败回滚,ServiceB.methodB() 是不会回滚的。如果 ServiceB.methodB() 失败回滚,如果他抛出的异常被 ServiceA.methodA() 捕获,ServiceA.methodA() 事务仍然可能提交。
如果当前在事务中,即以事务的形式运行,如果当前不再一个事务中,那么就以非事务的形式运行
必须在一个事务中运行。也就是说,他只能被一个父事务调用。否则,他就要抛出异常
当前不支持事务。比如 ServiceA.methodA() 的事务级别是 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,而 ServiceB.methodB() 的事务级别是 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED。
当执行到 ServiceB.methodB() 时,ServiceA.methodA() 的事务挂起,而他以非事务的状态运行完,再继续 ServiceA.methodA() 的事务。
不能在事务中运行。假设 ServiceA.methodA() 的事务级别是 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,而 ServiceB.methodB() 的事务级别是 PROPAGATION_NEVER ,那么 ServiceB.methodB() 就要抛出异常了。
下面我们将举例使用事务的方式更新用户的密码,当秘密的长度小于 5 时不更新。
resource/spring-transaction.xml 用来定义 transactionManager。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Enable Transaction -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>在 web.xml 中 springmvc 的 context 里加载加载事务配置。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- spring-mvc.xml ⽂件放在 resources 目录⾥里,
这个目录中的文件在项⺫编译后会被⾃动的复制到 classes 目录,
即在 classpath 中
-->
<param-value>
classpath:spring-mvc.xml
classpath:spring-transaction.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet><update id="updatePassword" ... > 是新增加的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC
"-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace 非常重要:必须是 Mapper 类的全路径-->
<mapper namespace="mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- [1] 简单的 JavaBean,直接使用 resultType: 数据库表的列与 JavaBean 的属性对应 -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="domain.User">
SELECT id, username, password FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="findUsers" resultType="domain.User">
SELECT id, username, password FROM user LIMIT ${offset}, ${count}
</select>
<update id="updatePassword" parameterType="domain.User">
UPDATE user SET password=#{password} WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>updatePassword() 函数是新增加的。
package mapper;
import domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
public User findUserById(int id);
// 使用 @Param 的方式传参数
public List<User> findUsers(@Param("offset") int offset, @Param("count") int count);
public void updatePassword(User user);
}updatePassword() 函数是新增加的,事务使用 annotation @Transactional。
package controller;
import domain.User;
import mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class MyBatisController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@RequestMapping("/user/{userId}")
@ResponseBody
public String findUser(@PathVariable Integer userId) {
// 查找一个 User
User user = userMapper.findUserById(userId);
List<User> users = userMapper.findUsers(1, 2);
System.out.println(users);
return user.toString();
}
@Transactional // 开启事务
// @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@RequestMapping(value="/user/{userId}/password/{password}")
@ResponseBody
public String updatePassword(@PathVariable int userId, @PathVariable String password) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(userId);
user.setPassword(password);
userMapper.updatePassword(user);
// 如果 password 的长度小于 5,抛出异常导致事务回滚
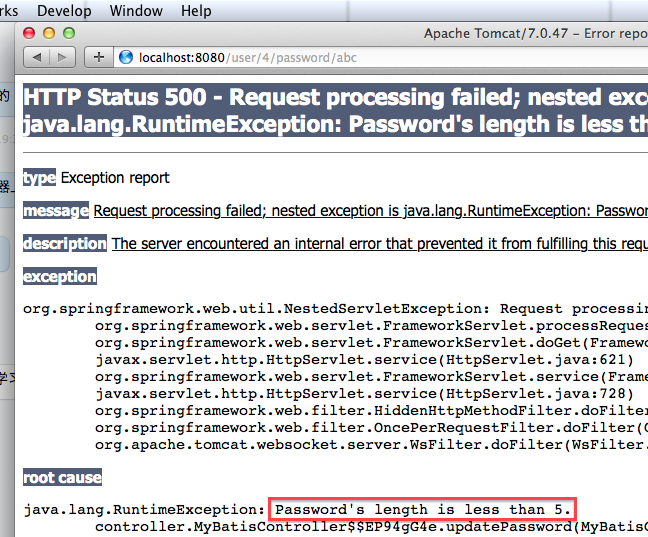
if (password.length() < 5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Password's length is less than 5.");
}
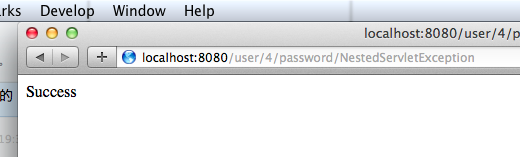
return "Success";
}
}
数据库里的数据

更新密码失败,因为新密码 abc 的长度小于 5
数据库里的数据
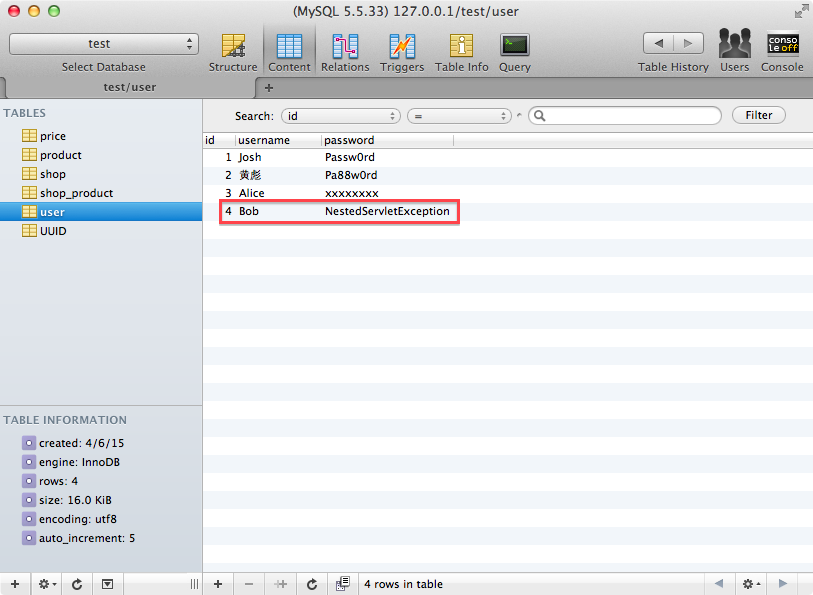
更新密码成功,因为新密码 NestedServletException 的长度大于 5
默认任何 RuntimeException 将触发事务回滚,但是任何 checked Exception 将不触发事务回滚,可以通过配置修改该规则,例如
@Transactional(noRollbackFor=RuntimeException.class)
@Transactional(RollbackFor=Exception.clas)